As a simple example, consider two particles with rest masses ![]() and
and
![]() , moving with speeds
, moving with speeds ![]() and
and ![]()
![]() , which collide and
coalesce [ see Figure 2.2 ]. What is the mass M and speed U of
the resulting particle.
, which collide and
coalesce [ see Figure 2.2 ]. What is the mass M and speed U of
the resulting particle.
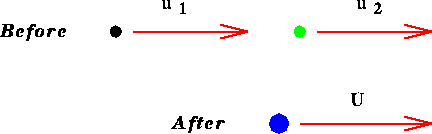
Figure 2.2: The colliding particles in Example 2.1.
The initial four- momenta are
![]()
where ![]() and
and
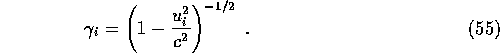
The final four- momentum is
![]()
Conservation of four- momentum gives
![]()
and squaring this relation gives
![]()
Now
![]()
and
![]()
This gives
![]()
For ![]() and
and ![]() ,
, ![]() which is the usual
Newtonian result.
From the x and t components of the four- momentum equation we have
which is the usual
Newtonian result.
From the x and t components of the four- momentum equation we have
![]()
Dividing we get
![]()
For ![]() and
and ![]() we obtain
we obtain
![]()